Table of Contents
Strep throat is more than just a sore throat. It’s a bacterial infection that can cause considerable discomfort and complications if left untreated. This common ailment is often mistaken for a typical sore throat caused by viruses, but there are distinct differences.
A sore throat is a general term that describes the pain, scratchiness, or irritation of the throat. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including viruses, bacteria, allergens, or environmental irritants. However, when we specifically talk about strep throat, we’re referring to an infection caused by the Group A Streptococcus bacteria. This infection predominantly affects the throat and tonsils, leading to symptoms that can be quite severe compared to a standard viral sore throat.
Understanding these differences is crucial because the treatments for strep throat and a viral sore throat are vastly different. While most sore throats can be managed with home remedies and over-the-counter medications, strep throat often requires a course of antibiotics to effectively combat the infection and prevent further complications.
In this guide, we’ll delve deeper into the causes, symptoms, and treatments of strep throat, providing you with comprehensive information to distinguish it from a common sore throat and understand the best ways to manage it.
What Causes Strep Throat?
Strep throat is primarily caused by a specific type of bacteria known as Group A Streptococcus. These bacteria are highly infectious and can lead to inflammation and pain in the throat and tonsils. While many people might think of a sore throat as a minor inconvenience, an infection caused by Group A strep is a different matter altogether.
These bacteria thrive in the nose and throat, making them easily transmissible through respiratory droplets. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, the bacteria are released into the air and can be inhaled by others. It’s not just about direct contact; sharing utensils, touching surfaces contaminated with the bacteria, or close contact with an infected person can all lead to contracting strep throat.
How Strep Throat Spreads
The contagious nature of strep throat is particularly concerning in environments like schools and daycare centers, where close contact and shared spaces are common. Children and adolescents are especially susceptible to this infection, not only because of their close contact with peers but also due to their still-developing immune systems.
It’s important to understand that strep throat can spread swiftly in these communal settings. That’s why outbreaks are often seen in schools and family homes, where one infected individual can unintentionally pass it on to others. In fact, strep throat is most common in children, though adults are certainly not immune to it.
Recognizing how strep throat spreads is crucial for its control and prevention. Simple measures, such as practicing good hygiene, washing hands frequently, and avoiding sharing personal items like toothbrushes and eating utensils, can significantly reduce the risk of spreading or contracting the infection.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Strep Throat

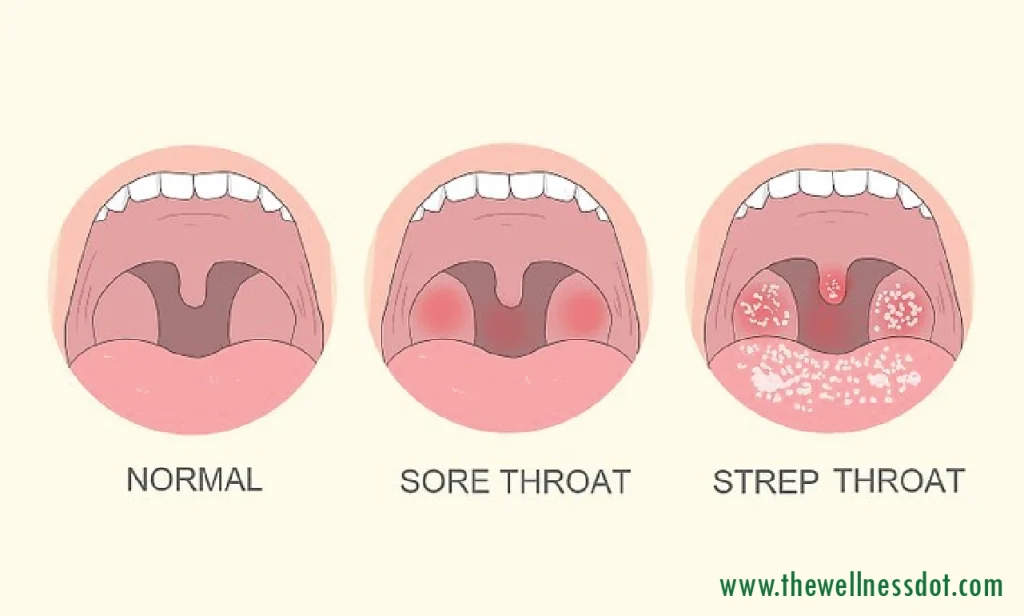
Identifying the symptoms of strep throat is crucial for effective treatment and to differentiate it from other types of throat infections. Strep throat is characterized by several distinct symptoms, which can vary between adults and children.
The most common symptoms of strep throat include:
- Intense throat pain that typically comes on suddenly
- Painful swallowing
- Red and swollen tonsils, sometimes with white patches or streaks of pus
- Tiny red spots (petechiae) on the roof of the mouth (the soft or hard palate)
- Swollen, tender lymph nodes at the front of the neck
Other symptoms, particularly in children, may include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Stomach pain, nausea, or vomiting, especially in younger children
- Rash (in cases of scarlet fever)
The Differences Between Strep Throat and Other Throat Illnesses
Unlike viral throat infections, strep throat typically does not involve cold-like symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, or a runny nose. The abrupt onset and severity of throat pain, coupled with fever without a cough, are strong indicators of strep throat rather than a viral infection. This distinction is essential as it influences the course of treatment: strep throat generally requires antibiotics, whereas viral infections do not.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s important to know when to seek medical attention for strep throat. If you or your child experience severe throat pain that doesn’t improve with over-the-counter remedies, or if symptoms are accompanied by high fever, difficulty breathing or swallowing, you should consult a healthcare provider.
Additionally, if symptoms such as a sore throat persist for more than a few days, it’s advisable to get a test for strep throat. Early diagnosis and treatment of strep throat can prevent complications and the spread of the infection to others. Children displaying symptoms should be seen by a doctor, especially if they have been exposed to someone with a confirmed case of strep throat, as they are more susceptible to complications.
Diagnosing Strep Throat
Diagnosing strep throat involves more than just recognizing symptoms; it requires specific tests to confirm the presence of Group A Streptococcus bacteria. Understanding the diagnostic process is key, as it guides the appropriate treatment approach.
Typically, healthcare professionals use two main tests to diagnose strep throat:
- Rapid Strep Test: This test provides quick results, often within minutes. It involves taking a throat swab from the back of the throat. If the test detects strep bacteria, the result is positive, and treatment can begin immediately.
- Throat Culture: If the rapid strep test is negative, but the symptoms strongly suggest strep throat, a throat culture might be recommended. This test is more sensitive and can detect strep bacteria that the rapid test might miss. The process involves culturing the bacteria from a throat swab in a laboratory, which can take a few days.
The Importance of Professional Diagnosis
It’s essential to understand that even if a rapid strep test is negative, a person can still have strep throat. In such cases, healthcare professionals may rely on clinical judgment or wait for the results of a throat culture before making a final diagnosis. This approach ensures that strep throat is not overlooked, especially in cases where symptoms are severe or typical of the infection.
Tests and Procedures
During a throat swab, a sterile swab is gently rubbed over the back of the throat, around the tonsils, and any other sore areas to collect a sample. This process is quick but might cause brief discomfort or gagging.
In the case of a throat culture, the collected bacteria are allowed to grow in a controlled environment. This process helps in accurately identifying the presence of Group A Streptococcus. The growth of strep bacteria in culture is a definitive indicator of strep throat, guiding the subsequent treatment plan.
Treating Strep Throat: The Role of Antibiotics

Once strep throat is diagnosed, treatment typically involves antibiotics, which play a crucial role in both curing the infection and preventing potential complications. Antibiotics are effective against strep throat because the condition is caused by bacteria, and these medications are designed to fight bacterial infections.
Why and When You Need Antibiotics
Antibiotics should be started as soon as strep throat is confirmed. The standard duration for antibiotic treatment is usually about 10 days. This duration is important because it ensures the complete elimination of the bacteria, reducing the risk of recurrence or complications. Stopping antibiotics too soon, even if symptoms improve, can lead to an incomplete treatment and possibly the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
The Importance of Completing Antibiotic Treatment
Completing the full course of antibiotics is essential to cure strep throat effectively and to prevent complications. One of the serious complications of untreated or improperly treated strep throat is rheumatic fever, a condition that can affect the heart, joints, nervous system, and skin. Antibiotic treatment significantly reduces the risk of these complications, making it a critical step in managing strep throat.
Alternative Treatments and Home Remedies
While antibiotics are necessary to treat strep throat, there are also various home remedies and alternative treatments that can help alleviate symptoms and provide comfort during recovery. These include:
- Gargling with warm salt water: This can help soothe a sore throat and reduce swelling.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids helps keep the throat moist and can reduce discomfort.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help ease throat pain and reduce fever.
- Rest: Adequate rest is essential for the body to fight off the infection effectively.
- Honey and lemon: Adding honey and lemon to warm water or tea can provide temporary relief from throat pain.
It’s important to note that while these remedies can help ease symptoms, they do not treat the underlying bacterial infection. Therefore, they should be used in conjunction with, and not as a replacement for, prescribed antibiotics.
Is Strep Throat Contagious?
One of the most important aspects to understand about strep throat is its highly contagious nature. Knowledge about how it spreads and appropriate preventative measures are crucial, especially in community settings like schools and daycare centers.
How Strep Throat Spreads
Strep throat is primarily spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The bacteria can also be transmitted by touching a surface contaminated with these droplets and then touching your nose or mouth. Close contact with an infected person, such as sharing food or drinks, can also lead to transmission.
Given the ease with which strep throat can spread, it’s particularly prevalent in environments where individuals are in close proximity, such as classrooms, family households, and daycare facilities.
When to Stay Home
If diagnosed with strep throat, it’s crucial to stay home from work, school, or other public places until you’ve been on antibiotics for at least 24 hours. This helps reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others. Additionally, individuals should remain at home if they are still experiencing symptoms, especially fever, as this indicates they may still be contagious.
Preventative Measures
Preventing the spread of strep throat involves several key practices:
- Good Hygiene: Regular hand washing with soap and water is one of the best ways to prevent the spread of infectious diseases, including strep throat. It’s especially important after coughing, sneezing, or before eating.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share drinking glasses, eating utensils, or other items that come in contact with the mouth.
- Cover Your Mouth and Nose: When coughing or sneezing, cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow to prevent the spread of droplets.
- Disinfecting Common Surfaces: Regularly clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, light switches, and toys, especially if someone in the home or school has been diagnosed with strep throat.
- Stay Informed: Be aware of the signs and symptoms of strep throat and seek medical attention promptly if you suspect you or your child may have the infection.
Understanding the contagious nature of strep throat and adhering to these preventive measures can significantly reduce the spread of the infection, particularly in group settings like schools and daycare centers.
Potential Complications of Strep Throat
While strep throat is commonly viewed as a relatively mild illness, it can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly and appropriately. Understanding these potential complications underscores the importance of timely medical intervention and adherence to prescribed treatments.
Complications Arising from Untreated Strep Throat
If left untreated, strep throat can lead to several significant health issues. Some of the notable complications include:
- Rheumatic Fever: This is a serious inflammatory condition that can affect the heart, joints, nervous system, and skin. It can develop if strep throat is not properly treated and is more common in children.
- Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis: This is a kidney disease that can occur after an untreated strep infection. It’s rare but can have serious implications for kidney function.
- Scarlet Fever: While scarlet fever itself is not typically severe, it indicates a more pronounced reaction to the strep bacteria and requires prompt treatment.
- Tonsillar Abscess: Untreated strep throat can lead to the development of an abscess around the tonsils, which may require surgical intervention.
The Importance of Timely and Appropriate Treatment
To prevent these complications, it is essential to start antibiotic treatment as soon as strep throat is diagnosed. Antibiotics help to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection, significantly reducing the risk of these serious health issues.
It’s also crucial to complete the entire course of prescribed antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. Stopping antibiotics early can lead to a resurgence of the infection and increase the risk of complications.
Monitoring for Complications
After treatment for strep throat, patients and caregivers should remain vigilant for any signs that may indicate complications, such as persistent fever, joint pains, unusual rashes, or worsening symptoms. If any of these signs appear, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
Understanding the potential complications of strep throat highlights the seriousness of this infection and the necessity of proper medical care. Timely diagnosis and treatment are key in managing strep throat and preventing its complications.
Key Takeaways
In this comprehensive guide on strep throat, we’ve covered several critical aspects of this common yet potentially serious bacterial infection. Here’s a summary of the most important points:
Summary of Strep Throat Causes and Treatment
- Strep Throat Causes: Strep throat is primarily caused by the Group A Streptococcus bacteria. It’s highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets, commonly affecting children and adolescents in communal settings like schools.
- Strep Throat Treatment: The primary treatment for strep throat is antibiotics, which are essential for curing the infection and preventing complications. It’s vital to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve earlier.
Recap of Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
- Symptoms: Strep throat typically presents with sudden and severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, red and swollen tonsils, fever, and sometimes a rash in children. It differs from a viral sore throat, which often includes coughing and a runny nose.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis is usually made using a rapid strep test or a throat culture, especially when initial tests are negative but clinical suspicion remains high.
- Treatment Options: Alongside antibiotics, symptom relief can be aided by home remedies like gargling salt water, staying hydrated, and using over-the-counter pain relievers. However, these should not replace antibiotic therapy.
The Importance of Understanding Strep Throat
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of strep throat, understanding its contagious nature, and the necessity of timely medical intervention are crucial for effective management of the infection. Awareness and adherence to treatment can prevent complications and ensure a swift recovery.
Remember, while strep throat is common, especially in children, it requires careful attention and should not be taken lightly due to its potential to lead to more serious health issues if left untreated.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How can I tell the difference between strep throat and a common sore throat?
- A1: Strep throat often presents with sudden, severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and fever without accompanying cold symptoms like coughing or a runny nose. On the other hand, a common sore throat, usually caused by a virus, may include these cold symptoms. If in doubt, it’s always best to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
Q2: What should I do if I or my child has symptoms of strep throat?
- A2: If you or your child exhibit symptoms of strep throat, it’s important to see a healthcare provider. They can conduct a rapid strep test or a throat culture to confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications and the spread of infection.
Q3: Are antibiotics always necessary for treating strep throat?
- A3: Yes, antibiotics are necessary to treat strep throat as it’s caused by bacteria. Antibiotics help eliminate the infection and prevent complications. It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
Q4: What home remedies can help alleviate strep throat symptoms?
- A4: While antibiotics are required to treat the infection, certain home remedies can provide symptom relief. These include gargling with warm salt water, staying hydrated, using over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, and getting plenty of rest. Honey and lemon in warm water or tea can also soothe a sore throat.
Q5: When is strep throat contagious, and how can I prevent spreading it?
- A5: Strep throat is most contagious when symptoms are at their peak. It’s advisable to stay home from school or work until at least 24 hours after starting antibiotics and when fever has subsided. Prevent spreading the bacteria by practicing good hygiene, not sharing personal items, covering your mouth when coughing or sneezing, and cleaning commonly touched surfaces regularly.
Q6: Can strep throat lead to more serious health issues?
- A6: Yes, if left untreated, strep throat can lead to complications like rheumatic fever, kidney inflammation, or tonsillar abscess. These complications are preventable with timely and appropriate antibiotic treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, strep throat is a common yet potentially serious condition caused by the Group A Streptococcus bacteria. It’s important to distinguish this bacterial infection from a typical viral sore throat due to its specific treatment needs and potential complications.
Key Recommendations for Managing and Preventing Strep Throat
- Seek Timely Medical Advice: If you suspect you or your child has strep throat, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Adhere to Treatment: If diagnosed with strep throat, completing the full course of prescribed antibiotics is crucial, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular hand washing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and not sharing personal items can help prevent the spread of the infection.
- Stay Informed: Recognizing the signs and symptoms of strep throat and understanding its contagious nature can help in making informed decisions about when to seek medical care and how to prevent its spread.
Encouragement for Seeking Professional Advice
Especially in cases of recurrent sore throat in children, professional medical advice is invaluable. Children are more prone to complications from strep throat, and recurring infections may need further investigation. Do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider if you’re concerned about repeated instances of sore throat in your child. Early intervention can prevent complications and ensure the health and well-being of your child.
Remember, while home remedies can alleviate symptoms, they are not a substitute for professional medical treatment. Staying proactive in health management and seeking timely medical advice are the best strategies to effectively manage and prevent strep throat.